What Describes Best the Structure That Rotifers Are Named for
The excretory structures of rotifers are Flame cells. Complete digestive system regionally specialized.

Bdelloid Rotifer Morphology A A Ricciae Individual In Phase Download Scientific Diagram
The rapid movement of the cilia in some species makes them appear to whirl like a wheel.

. Rotifers are so named because the circular arrangement of moving cilia tiny hairlike structures at the front end resembles a rotating wheel. Rotifers are thus multicellular creatures who make make their living at the scale of unicellular protists. They have also been called wheel animalcules from the corona which is composed of several ciliated tufts around the mouth.
The most distinctive feature of rotifers is the presence of corona on the head. There are 2011 species of Rotifers in 132 genera and 34 families. Rotifer wheel animacule Microscopic metazoan found mainly in freshwater.
The rotifers wheel-bearer belong to a group of microscopic about 100 µm to 2 mm mostly aquatic animals that get their name from the coronaa pair of ciliated feeding structures that appear to rotate when viewed under the light microscope. Because they are among the smallest of freshwater metazoans most are between 50 and 2000 μm rotifers are often mistaken for protists. So the correct answer is Flame cells.
Males generally reduced in number or absent. Rotifers are an important part of the freshwater zooplankton. They are also called wheeled animals.
Rotifers get their name derived from Latin and meaning wheel-bearer. Although common in freshwater on all continents some species occur in salt water or brackish water whereas others live in damp moss or lichens. Digestive system with a highly muscular pharynx called mastax lined internally with cuticle and within mastax is a rigid structure or jaws called trophi used for grasping and grinding the prey.
Rotifers are ammonotelic animals and have two typical protonephridia in the pseudocoel. First described by Anton Van Leeuwenoek in the late 1600s Rotifera is a small phylum of about 2000 species of tiny bilaterally symmetrical unsegmented animals traditionally described as pseudocoelomate. The rotifers wheel-bearer belong to a group of microscopic about 100 µm to 2 mm mostly aquatic animals that get their name from the corona a pair of ciliated feeding structures that appear to rotate when viewed under the light microscope Figure.
Most of them are aquatic living in freshwater bodies though a few are also found in saltwater. Number of currently described and taxonomically accepted marine species in this clade Appeltans et al. Protonephridia with flame cells.
As the name suggests wheel animalswheel-bearer Rotifers are characterized by a ciliated corona located at the anterior end head part of the organism. The name rotifer means wheel-bearer in Latin. This helps create a current that sweeps food into the mouth.
The flame cells function like a kidney removing nitrogenous waste. Rotifers Phylum Rotifera Less than one millimetre in length the name for these tiny cylindrical creatures comes from a double row of hairs that surrounds their mouth. Although their taxonomic status is currently in flux one treatment places the rotifers in.
Although it resembles ciliate protozoan it is many-celled with a general body structure similar to that of a simple worm. There is a protective lorica round its body and a foot. The nervous system consists of a brain comprising of a dorsal ganglionic mass lying over the mastax which gives rise to a number of nerves that extend to different parts of the body.
Rotifers may be elongated or round and are identified by a crown of cilia around the mouth. This phylum has been around since the eocene epoch. The coronal cilia also help to pull the animal when unattached through the water.
The name rotifer is derived from the Latin word meaning wheel-bearer. This gave the rotifers their old name of wheel animalules. Rotifera Rotifers is a phylum of animals.
Brachionus quadridentatus Colurella adriatica Habrotrocha angusticollis Cephalodella gibba. Currently about 2000 species of the phylum have been identified. Posterior end with toes and adhesive glands.
Cuticle secreted within epidermis and never moulted. Epidermis sometimes secretes cuticle and sometimes has lorica shell structure syncytial epidermis Describe the external body features of rotifers head trunk tail. Name 7 characteristics of the phylum Rotifera Triploblastic bilateral unsegmented pseudocoelomate.
They eat dead bacteria algae and protozoans. Historically referred to as the Wheel Animalcule or Wheel Animal rotifers were named for the shimmering rings of tiny beating cilia that draw food into their mouths. The pharynx has a powerful muscular wall and contains tiny calcified jaw-like structures called trophi which are the only fossilizable parts of a rotifer.
The most distinctive feature of rotifers is the presence of corona which is a ciliated structure present on the head. Posterior foot of Phylum Rotifera has two toes. Rotifers are either dioecious or parthenogenetic females.
Inside the lorica are the usual organs in miniturised form. Rotifers consist of only a few hundred cells but are complex creatures considering that they are generally the same size as many protozoans one-celled organisms. Rotifers use this ring of cilia called a corona for feeding on organic waste algae and protozoans.
The structure is called a corona which is Latin for crown. When they arent attached to a substrate rotifers also. The shape of the trophi varies between different species depending partly on the nature of their diet.
It is named so because it has two rings of cilia hair-like structures on its head which on moving appear like two rotating wheels. Examples of Rotifers include. Foot with cement glands.
A brain an eye-spot jaws stomach kidneys urinary bladder. This makes reference to the crown of cilia around the mouth of the rotifer. When observed the beating of the cilia resembles the rotation of a wheel.
The beating of the cilia looks quite often like a wheel spinning. Rotifers have a number of unusual features. The mastax is a bulb-like structure consisting of many muscles which control a complex set of jaws which consists of hardened proteins.
This is a ciliated structure that facilitates movement allows feeding and from which the animals acquired their older name. Rotifers possess a structure called a mastax which is unique in the animal kingdom. Of rotifers is only beginning.
Solution Verified by Toppr Correct option is C Rotifers are microscopic aquatic animals belonging to phylum rotifera. The word rotifer means wheel-bearer which is owed to the cilia that surround the mouth of the animal. The hairs on the corona of most rotifers beat to draw a current of water into the mouth which carries with it small animals and particles of food.
Anterior end often has a ciliated organ called a corona.

Phylum Rotifera Biology For Majors Ii

Bdelloid Rotifer Morphology A A Ricciae Individual In Phase Download Scientific Diagram

Phylum Rotifera Biology For Majors Ii
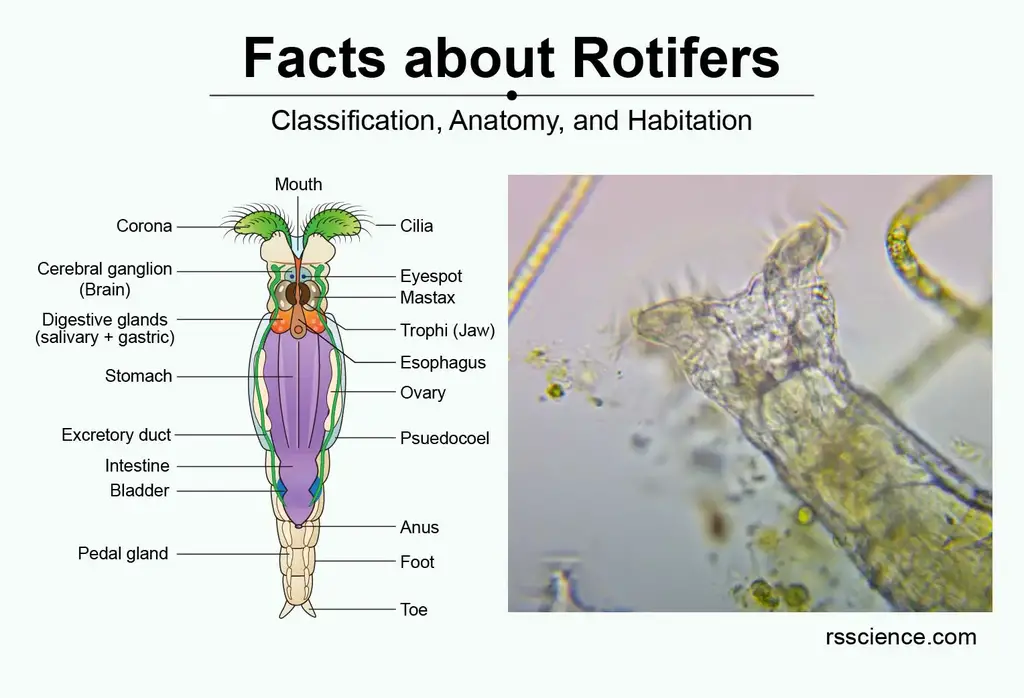
Facts About Rotifers Amazing Microscopic Animals Under The Microscope
No comments for "What Describes Best the Structure That Rotifers Are Named for"
Post a Comment